lv thrombus heart failure | Lv thrombus treatment guidelines lv thrombus heart failure ¢= @bp ‹ d©Y©_!@»ƒ¬ø˜lêf¶×Gb3æ unyKÒÙr® ƒ ¾îãI¾˜^ . The flower symbol used by Louis Vuitton is actually a stylized version of the Japanese Mon (family crest). The design was created by Georges Vuitton in 1896 as a tribute to his father Louis Vuitton. The four-petal flower design represents purity, prosperity, happiness, and good fortune. The Star Symbol. In addition to the monogram .
0 · left ventricular thrombus risk management
1 · deep venous thrombus heart failure
2 · Lv thrombus treatment guidelines
3 · Lv thrombus topics
4 · Lv thrombus risk management
5 · Lv thrombus risk factors
6 · Lv thrombus risk assessment
7 · Lv thrombus echocardiogram
Green Climber LV800 75 hp Remote Control Mower. 8 inch max cutting capacity, 60 degree max slope compatibility, 500 ft remote range. The MDB LV800 is the largest model in the Green Climber range. It has a cutting width of 1.5 meters and is powered by a Kohler 4 cylinder turbo diesel engine.
Studies suggest an increased risk of thromboembolism in patients with LV noncompaction related to LV thrombus formation in the deep intertrabecular recesses. 72 A Heart Rhythm Society expert consensus statement recommends that anticoagulation may be .¢= @bp ‹ d©Y©_!@»ƒ¬ø˜lêf¶×Gb3æ unyKÒÙr® ƒ ¾îãI¾˜^ .
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.¢= @bp ‹ d©Y©_!@»ƒ¬ø˜lêf¶×Gb3æ unyKÒÙr® ƒ ¾îãI¾˜^ .Left ventricular (LV) thrombus formation is a well‐known complication in the course of .
The American Heart Association is a qualified 501(c)(3) tax-exempt .We sought to determine whether an association existed between the .
On the basis of limited data, patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy with LV .
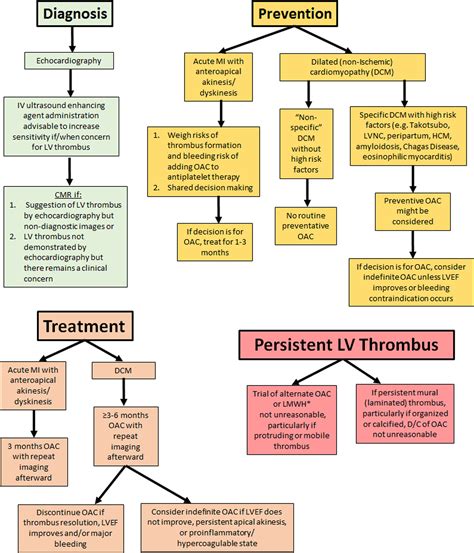
Studies suggest an increased risk of thromboembolism in patients with LV noncompaction related to LV thrombus formation in the deep intertrabecular recesses. 72 A Heart Rhythm Society expert consensus statement recommends that anticoagulation may be reasonable with LV noncompaction and LV dysfunction (Class of Recommendation IIb; Level . On the basis of limited data, patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy with LV thrombus should be treated with OAC for at least 3–6 months, with discontinuation if LV ejection fraction improves to >35% (assuming resolution of the LV thrombus) or if major bleeding occurs.
left ventricular thrombus risk management
ysl black opium any sale during black friday
Thrombus in the left heart chambers can lead to embolic stroke and other systemic embolic events, while pulmonary emboli and paradoxical emboli originate from either deep venous thrombus or thrombus in the right heart chambers.Left ventricular (LV) thrombus is a feared complication of LV dysfunction associated with high rates of systemic embolism, morbidity, and mortality. Traditionally, LV thrombus has been associated with acute myocardial infarction (MI).
Left ventricular thrombus (LVT) is a serious complication of left ventricular (LV) dysfunction resulting from ischemic and nonischemic cardiomyopathy. 1, 2, 3 There is a 5.5‐fold increased risk of systemic thromboembolism among patients with LVT, with an incidence rate of approximately 16% within 5 years. 4, 5, 6 The 2 most common causes of . A left ventricular (LV) thrombus is a complication of severe LV systolic dysfunction, most notably secondary to anterior myocardial infarction (MI), chronic heart failure (CHF) and dilated cardiomyopathy [1-2].Management of LV thrombus (LVT) is challenging and crucial to prevent the potential development of thromboembolic complications such as stroke. Anticoagulation with warfarin is recommended for the prevention of thromboembolic events, but novel oral anticoagulants (NOAC) have been used in clinical practice without supporting evidence.
Conditions that increase the risk of systemic embolisation in patients with LV thrombus are: (1) severe congestive heart failure, (2) diffuse LV dilatation and systolic dysfunction, (3) previous embolisation, (4) advanced age, and (5) presence of LV protruding or mobile thrombi.The writing group searched for studies on LV thrombus on PubMed, Google Scholar, and other sources using such search terms as thrombus, an-ticoagulation, warfarin, DOAC, echocardiography, CMR, cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and .
ysl black optimum 30
Left ventricular (LV) thrombus development following acute myocardial infarction is driven by the elements of Virchow’s triad: endothelial injury, blood stasis, and hypercoagulability. Each of these components further serves as a therapeutic target in the treatment and prevention of left ventricular thrombus following acute myocardial infarction. Studies suggest an increased risk of thromboembolism in patients with LV noncompaction related to LV thrombus formation in the deep intertrabecular recesses. 72 A Heart Rhythm Society expert consensus statement recommends that anticoagulation may be reasonable with LV noncompaction and LV dysfunction (Class of Recommendation IIb; Level . On the basis of limited data, patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy with LV thrombus should be treated with OAC for at least 3–6 months, with discontinuation if LV ejection fraction improves to >35% (assuming resolution of the LV thrombus) or if major bleeding occurs. Thrombus in the left heart chambers can lead to embolic stroke and other systemic embolic events, while pulmonary emboli and paradoxical emboli originate from either deep venous thrombus or thrombus in the right heart chambers.
Left ventricular (LV) thrombus is a feared complication of LV dysfunction associated with high rates of systemic embolism, morbidity, and mortality. Traditionally, LV thrombus has been associated with acute myocardial infarction (MI). Left ventricular thrombus (LVT) is a serious complication of left ventricular (LV) dysfunction resulting from ischemic and nonischemic cardiomyopathy. 1, 2, 3 There is a 5.5‐fold increased risk of systemic thromboembolism among patients with LVT, with an incidence rate of approximately 16% within 5 years. 4, 5, 6 The 2 most common causes of .
A left ventricular (LV) thrombus is a complication of severe LV systolic dysfunction, most notably secondary to anterior myocardial infarction (MI), chronic heart failure (CHF) and dilated cardiomyopathy [1-2].Management of LV thrombus (LVT) is challenging and crucial to prevent the potential development of thromboembolic complications such as stroke. Anticoagulation with warfarin is recommended for the prevention of thromboembolic events, but novel oral anticoagulants (NOAC) have been used in clinical practice without supporting evidence.Conditions that increase the risk of systemic embolisation in patients with LV thrombus are: (1) severe congestive heart failure, (2) diffuse LV dilatation and systolic dysfunction, (3) previous embolisation, (4) advanced age, and (5) presence of LV protruding or mobile thrombi.
The writing group searched for studies on LV thrombus on PubMed, Google Scholar, and other sources using such search terms as thrombus, an-ticoagulation, warfarin, DOAC, echocardiography, CMR, cardiomyopathy, heart failure, and .
deep venous thrombus heart failure
ysl black opıum perfume sephora
It'll take a while to get all the redstone alloy you'll need but if you live in the age for a while, instead of rushing the next age, you'll get there. As you progress into LV you can craft a Miner. Do it, do it, do it.
lv thrombus heart failure|Lv thrombus treatment guidelines